原理
Reactor 原理整理
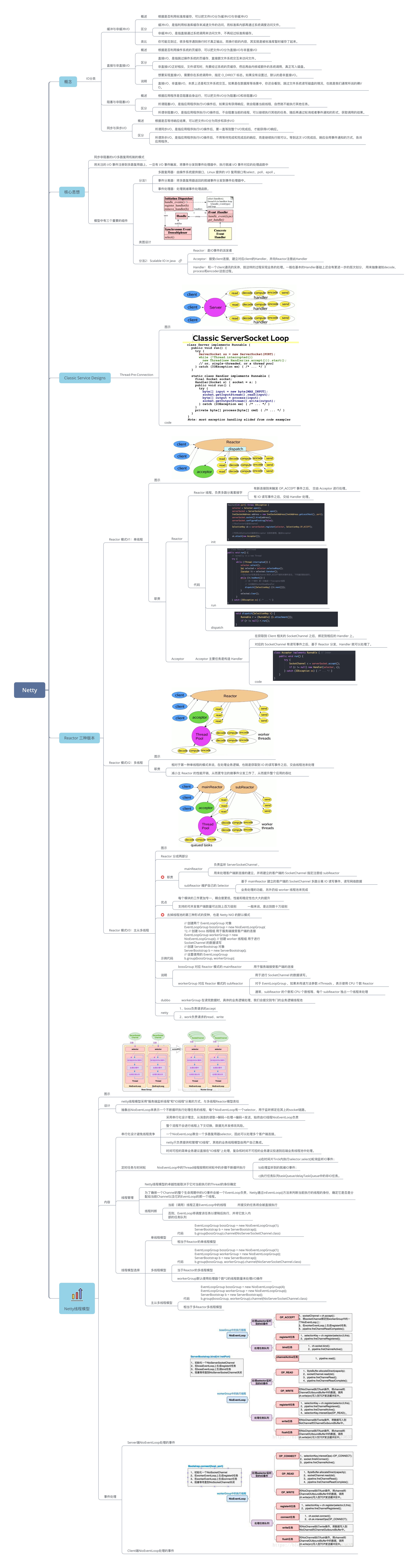
附件
Reactor V1 示例代码
Reactor
public class Reactor implements Runnable {
final Selector selector;
final ServerSocketChannel serverSocket;
Reactor(int port) throws IOException {
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), port);
serverSocket.socket().bind(address);
serverSocket.configureBlocking(false);
//向selector注册该channel
SelectionKey sk = serverSocket.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//利用sk的attache功能绑定Acceptor 如果有事情,触发Acceptor
sk.attach(new Acceptor());
}
// class Reactor continued
public void run() {
// normally in a new Thread
try {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
selector.select();
Set selected = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = selected.iterator();
//Selector如果发现channel有OP_ACCEPT或READ事件发生,下列遍历就会进行。
while (it.hasNext()) {
// 来一个事件 第一次触发一个accepter线程
// 以后触发SocketReadHandler
dispatch((SelectionKey) (it.next()));
}
selected.clear();
}
} catch (IOException ex) { /* ... */ }
}
void dispatch(SelectionKey k) {
Runnable r = (Runnable) (k.attachment());
if (r != null) r.run();
}
class Acceptor implements Runnable { // inner
public void run() {
try {
SocketChannel c = serverSocket.accept();
if (c != null) new Handler(selector, c);
} catch (IOException ex) { /* ... */ }
}
}
}
Handler
public class Handler {
final SocketChannel socket;
final SelectionKey sk;
ByteBuffer input = ByteBuffer.allocate(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
ByteBuffer output = ByteBuffer.allocate(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
static final int READING = 0, SENDING = 1;
int state = READING;
public Handler(Selector sel, SocketChannel c) throws IOException {
socket = c;
//设置为非阻塞模式
c.configureBlocking(false);
//此处的0,表示不关注任何时间
sk = socket.register(sel, 0);
//将SelectionKey绑定为本Handler 下一步有事件触发时,将调用本类的run方法
sk.attach(this);
//将SelectionKey标记为可读,以便读取,不可关注可写事件
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
sel.wakeup();
}
boolean inputIsComplete() {
return false;
}
boolean outputIsComplete() {
return false;
}
//这里可以通过线程池处理数据
void process() {
}
public void run() {
try {
if (state == READING) {
read();
} else if (state == SENDING) {
send();
}
} catch (IOException ex) { /* ... */ }
}
void read() throws IOException {
socket.read(input);
if (inputIsComplete()) {
process();
state = SENDING;
// Normally also do first write now
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
void send() throws IOException {
socket.write(output);
if (outputIsComplete()) {
//
sk.cancel();
}
}
}