简介
本文在《拍拍贷基础框架团队博客-feign源码解析》的基础上,进行了版本更新、修改和补充
Feign makes writing java http clients easier
Feign 是一款 java 的 Restful 客户端组件,Feign使得 Java HTTP 客户端编写更方便。Feign 灵感来源于Retrofit, JAXRS-2.0和 WebSocket。Feign 最初是为了降低统一绑定Denominator 到 HTTP API 的复杂度,不区分是否支持 ReSTfulness。
feign 的基本原理是在接口方法上加注解,定义 rest 请求,构造出接口的动态代理对象,然后通过调用接口方法就可以发送 http 请求,并且自动解析 http 响应为方法返回值,极大的简化了客户端调用 rest api 的代码。
基本实现
动态代理流程
接口的动态代理主要接口和类的类图

Feign 构建接口动态代理
Feign’s purpose is to ease development against http apis that feign restfulness. In implementation, Feign is a factory for generating targeted http apis.
构建的接口动态代理对象是通过 Feign.builder() 生成 Feign.Builder 的构造者对象,然后设置相关的参数,再调用 target 方法构造的。Feign.Builder 的参数包括:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
// 拦截器,组装完 RequestTemplate,发请求之前的拦截处理 RequestTemplate
private final List<RequestInterceptor> requestInterceptors =
new ArrayList<RequestInterceptor>();
// 日志级别
private Logger.Level logLevel = Logger.Level.NONE;
// 契约模型,默认为Contract.Default,用户创建MethodMetadata,用spring cloud就是扩展这个实现springMVC注解
private Contract contract = new Contract.Default();
// 客户端,默认为Client.Default,可以扩展ApacheHttpClient,OKHttpClient,RibbonClient等
private Client client = new Client.Default(null, null);
// 重试设置,默认不设置
private Retryer retryer = new Retryer.Default();
// 日志,可以接入Slf4j
private Logger logger = new NoOpLogger();
// 编码器,用于body的编码
private Encoder encoder = new Encoder.Default();
// 解码器,用户response的解码
private Decoder decoder = new Decoder.Default();
// 用@QueryMap注解的参数编码器
private QueryMapEncoder queryMapEncoder = new QueryMapEncoder.Default();
// 请求错误解码器
private ErrorDecoder errorDecoder = new ErrorDecoder.Default();
// 参数配置,主要是超时时间之类的
private Options options = new Options();
// 动态代理工厂
private InvocationHandlerFactory invocationHandlerFactory =
new InvocationHandlerFactory.Default();
// 是否decode404
private boolean decode404;
// 该标志表示在解码消息完成后不应自动关闭响应。如果您计划将响应处理为延迟评估的构造,则应设置此项
private boolean closeAfterDecode = true;
// 异常传播策略
private ExceptionPropagationPolicy propagationPolicy = NONE;
这块是一个典型的构造者模式,target方法内部先调用build方法新建一个ReflectFeign对象,然后调用ReflectFeign的newInstance方法创建动态代理,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// 默认使用 HardCodedTarget
public <T> T target(Class<T> apiType, String url) {
return target(new HardCodedTarget<T>(apiType, url));
}
public <T> T target(Target<T> target) {
return build().newInstance(target);
}
public Feign build() {
SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory synchronousMethodHandlerFactory =
new SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory(client, retryer, requestInterceptors, logger,
logLevel, decode404, closeAfterDecode, propagationPolicy);
ParseHandlersByName handlersByName =
new ParseHandlersByName(contract, options, encoder, decoder, queryMapEncoder,
errorDecoder, synchronousMethodHandlerFactory);
// handlersByName 将所有参数进行封装,并提供解析接口方法的逻辑
// invocationHandlerFactory 是 Builder 的属性,默认值是InvocationHandlerFactory.Default,用创建 java 动态代理的 InvocationHandler 实现
return new ReflectiveFeign(handlersByName, invocationHandlerFactory, queryMapEncoder);
}
ReflectiveFeign 类
ReflectiveFeign 构造函数有三个参数:
- ParseHandlersByName:将 builder 所有参数进行封装,并提供解析接口方法的逻辑
- InvocationHandlerFactory:java 动态代理的 InvocationHandler 的工厂类,默认值是InvocationHandlerFactory.Default
- QueryMapEncoder:接口参数注解 @QueryMap 时,参数的编码器
ReflectiveFeign.newInstance 方法创建接口动态代理对象:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
@Override
public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) {
// targetToHandlersByName 是构造器传入的 ParseHandlersByName 对象,根据target 对象生成 MethodHandler 映射。里面包含:Contract、Options、Encoder、Decoder、ErrorDecoder、QueryMapEncoder及SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory
Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>();
List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>();
// 遍历接口所有方法,构建Method->MethodHandler的映射
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
continue;
} else if (Util.isDefault(method)) {
// 接口default方法的Handler,这类方法直接调用
DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);
defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);
methodToHandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
// 这里 factory 是构造其中传入的,创建 InvocationHandler
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
// java的动态代理
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[] {target.type()}, handler);
// 将default方法直接绑定到动态代理上
for (DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}
这段代码主要的逻辑是:
- 创建 MethodHandler 的映射,这里创建的是实现类 SynchronousMethodHandler
- 通过 InvocationHandlerFatory 创建 InvocationHandler
- 绑定接口的 default 方法,通过 DefaultMethodHandler 绑定
- 类图中已经画出,SynchronousMethodHandler 和 DefaultMethodHandler 实现了
InvocationHandlerFactory.MethodHandler 接口,动态代理对象调用方法时,如果是default方法,会直接调用接口方法,因为这里将接口的default方法绑定到动态代理对象上了,其他方法根据方法签名找到 SynchronousMethodHandler 对象,调用其 invoke 方法。
附录:Java MethodHandle
Java7在JSR 292中增加了对动态类型语言的支持,使得java也可以像C语言那样将方法作为参数传递。 在java.lang.invoke包中MethodHandle作用类似于反射中的Method类,但它比Method类要更加灵活和轻量级。 Reflection是java api层面的反射调用,而MethodHandle则是jvm层面支持调用。因此Reflection是重量级,MethodHandle则是轻量级的。下面来看看怎么使用
通过MethodHandle进行方法调用一般需要:
- 创建 MethodType 对象,指定方法的签名(即方法参数以及方法返回值的类型)。
- 在 MethodHandles.Lookup 中查找类型为MethodType的MethodHandle;
- 传入方法参数并调用 MethodHandle.invoke 或者 MethodHandle.invokeExact方法。
创建MethodHandler方法处理器
SynchronousMethodHandler 是 feign 组件的核心,接口方法调用转换为 http 请求和解析http 响应都是通过 SynchronousMethodHandler 来执行的,相关类图如下:

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public Map<String, MethodHandler> apply(Target key) {
// 通过contract解析接口方法,生成MethodMetadata列表,默认的contract解析Feign自定义的http注解
List<MethodMetadata> metadata = contract.parseAndValidatateMetadata(key.type());
Map<String, MethodHandler> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, MethodHandler>();
for (MethodMetadata md : metadata) {
BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs buildTemplate;
if (!md.formParams().isEmpty() && md.template().bodyTemplate() == null) {
buildTemplate = new BuildFormEncodedTemplateFromArgs(md, encoder, queryMapEncoder);
} else if (md.bodyIndex() != null) {
buildTemplate = new BuildEncodedTemplateFromArgs(md, encoder, queryMapEncoder);
} else {
buildTemplate = new BuildTemplateByResolvingArgs(md, queryMapEncoder);
}
result.put(md.configKey(),
factory.create(key, md, buildTemplate, options, decoder, errorDecoder));
}
return result;
}
为了直观理解 targetToHandlersByName.apply(target) 处逻辑,进行了断点抓取
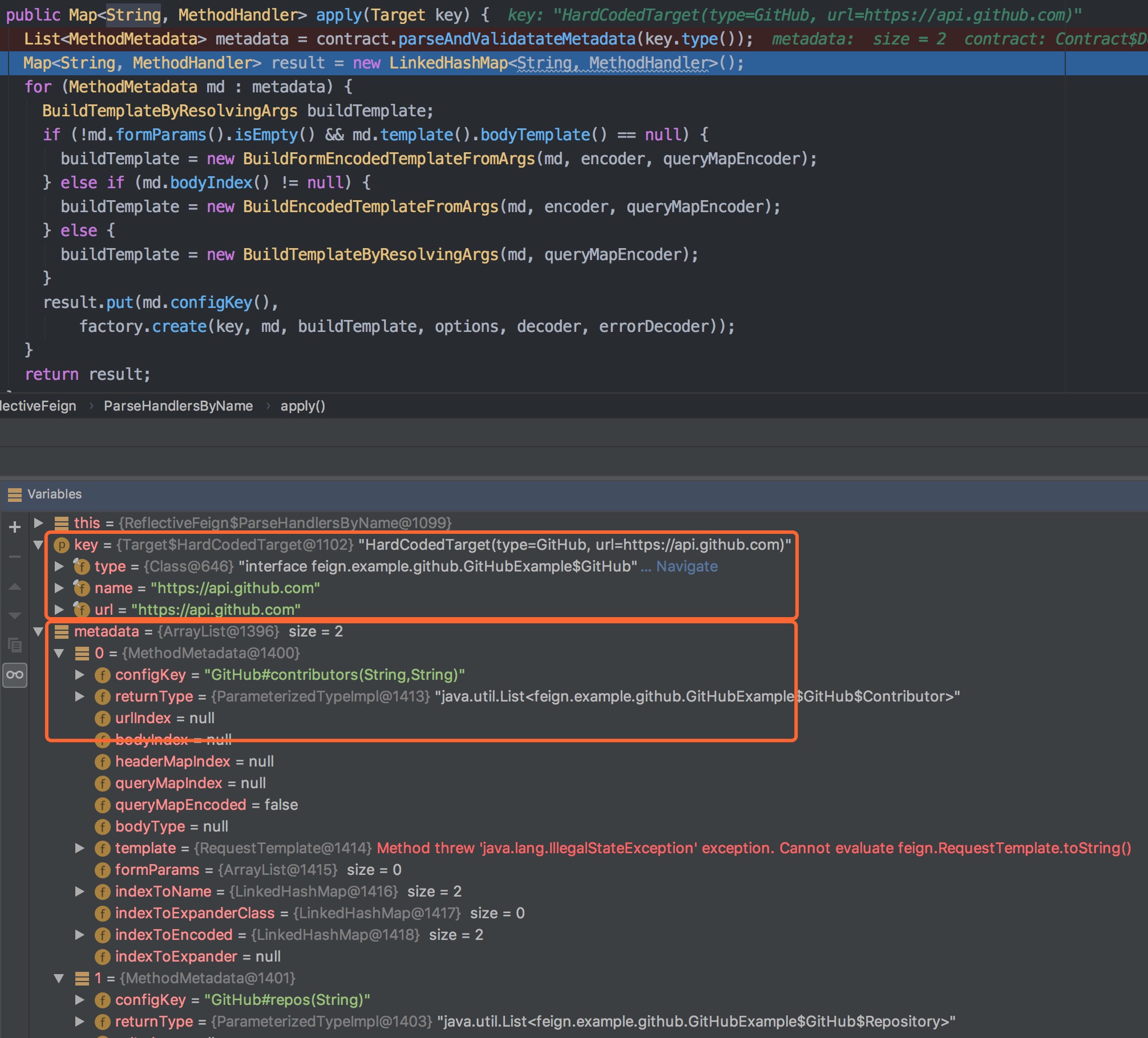
这段代码的逻辑是:
- 通过Contract解析接口方法,生成MethodMetadata,默认的Contract解析Feign自定义的http注解
- 根据MethodMetadata方法元数据生成特定的RequestTemplate的工厂
- 使用SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory工厂创建SynchronousMethodHandler 这里有两个工厂不要搞混淆了,SynchronousMethodHandler工厂和RequestTemplate工厂,SynchronousMethodHandler的属性包含RequestTemplate工厂
Contract 及 MethodMetadata
Contract 类:定义注释和值在接口上的有效性。
Defines what annotations and values are valid on interfaces.
MethodMetadata 类:解析和记录接口上的元数据信息
feign默认的解析器是Contract.Default继承了Contract.BaseContract,解析生成MethodMetadata方法入口:
abstract class BaseContract implements Contract 源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
abstract class BaseContract implements Contract {
@Override
public List<MethodMetadata> parseAndValidatateMetadata(Class<?> targetType) {
// checkState(...);
Map<String, MethodMetadata> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, MethodMetadata>();
for (Method method : targetType.getMethods()) {
MethodMetadata metadata = parseAndValidateMetadata(targetType, method);
// checkState(...);
result.put(metadata.configKey(), metadata);
}
return new ArrayList<>(result.values());
}
/**
* Called indirectly by {@link #parseAndValidatateMetadata(Class)}.
*/
protected MethodMetadata parseAndValidateMetadata(Class<?> targetType, Method method) {
MethodMetadata data = new MethodMetadata();
data.returnType(Types.resolve(targetType, targetType, method.getGenericReturnType()));
data.configKey(Feign.configKey(targetType, method));
if (targetType.getInterfaces().length == 1) {
processAnnotationOnClass(data, targetType.getInterfaces()[0]);
}
// 处理Class上的注解
processAnnotationOnClass(data, targetType);
for (Annotation methodAnnotation : method.getAnnotations()) {
// 处理方法注解
processAnnotationOnMethod(data, methodAnnotation, method);
}
// checkState(...);
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
// 方法参数注解
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
int count = parameterAnnotations.length;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
boolean isHttpAnnotation = false;
if (parameterAnnotations[i] != null) {
isHttpAnnotation = processAnnotationsOnParameter(data, parameterAnnotations[i], i);
}
if (parameterTypes[i] == URI.class) {
// 参数类型是URI,后面构造http请求时,使用该URI
data.urlIndex(i);
} else if (!isHttpAnnotation) {
checkState(data.formParams().isEmpty(),
"Body parameters cannot be used with form parameters.");
checkState(data.bodyIndex() == null, "Method has too many Body parameters: %s", method);
// 如果没有被http注解,就是body参数
data.bodyIndex(i);
data.bodyType(Types.resolve(targetType, targetType, genericParameterTypes[i]));
}
}
if (data.headerMapIndex() != null) {
// @HeaderMap注解的参数必须是Map,key类型必须是String
checkMapString("HeaderMap", parameterTypes[data.headerMapIndex()],
genericParameterTypes[data.headerMapIndex()]);
}
if (data.queryMapIndex() != null) {
if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterTypes[data.queryMapIndex()])) {
// @QueryMap注解的参数如果是Map,key类型必须是String
checkMapKeys("QueryMap", genericParameterTypes[data.queryMapIndex()]);
}
}
return data;
}
private static void checkMapString(String name, Class<?> type, Type genericType) {
// checkState(...);
}
private static void checkMapKeys(String name, Type genericType) {
// ...
}
/**
* Called by parseAndValidateMetadata twice, first on the declaring class, then on the target
* type (unless they are the same).
*
* @param data metadata collected so far relating to the current java method.
* @param clz the class to process
*/
protected abstract void processAnnotationOnClass(MethodMetadata data, Class<?> clz);
/**
* @param data metadata collected so far relating to the current java method.
* @param annotation annotations present on the current method annotation.
* @param method method currently being processed.
*/
protected abstract void processAnnotationOnMethod(MethodMetadata data,
Annotation annotation,
Method method);
/**
* @param data metadata collected so far relating to the current java method.
* @param annotations annotations present on the current parameter annotation.
* @param paramIndex if you find a name in {@code annotations}, call
* {@link #nameParam(MethodMetadata, String, int)} with this as the last parameter.
* @return true if you called {@link #nameParam(MethodMetadata, String, int)} after finding an
* http-relevant annotation.
*/
protected abstract boolean processAnnotationsOnParameter(MethodMetadata data,
Annotation[] annotations,
int paramIndex);
/**
* links a parameter name to its index in the method signature.
*/
protected void nameParam(MethodMetadata data, String name, int i) {
Collection<String> names =
data.indexToName().containsKey(i) ? data.indexToName().get(i) : new ArrayList<String>();
names.add(name);
data.indexToName().put(i, names);
}
}
class Default extends BaseContract 源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
class Default extends BaseContract {
static final Pattern REQUEST_LINE_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("^([A-Z]+)[ ]*(.*)$");
@Override
protected void processAnnotationOnClass(MethodMetadata data, Class<?> targetType) {
if (targetType.isAnnotationPresent(Headers.class)) {
// @Headers注解
String[] headersOnType = targetType.getAnnotation(Headers.class).value();
// checkState(...);
// header解析成map,加到MethodMetadata中
Map<String, Collection<String>> headers = toMap(headersOnType);
headers.putAll(data.template().headers());
data.template().headers(null); // to clear
data.template().headers(headers);
}
}
@Override
protected void processAnnotationOnMethod(MethodMetadata data,
Annotation methodAnnotation,
Method method) {
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = methodAnnotation.annotationType();
if (annotationType == RequestLine.class) {
// @RequestLine注解
String requestLine = RequestLine.class.cast(methodAnnotation).value();
// checkState(...);
Matcher requestLineMatcher = REQUEST_LINE_PATTERN.matcher(requestLine);
if (!requestLineMatcher.find()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format(
"RequestLine annotation didn't start with an HTTP verb on method %s",
method.getName()));
} else {
data.template().method(HttpMethod.valueOf(requestLineMatcher.group(1)));
data.template().uri(requestLineMatcher.group(2));
}
data.template().decodeSlash(RequestLine.class.cast(methodAnnotation).decodeSlash());
data.template()
.collectionFormat(RequestLine.class.cast(methodAnnotation).collectionFormat());
} else if (annotationType == Body.class) {
// @Body注解
String body = Body.class.cast(methodAnnotation).value();
checkState(emptyToNull(body) != null, "Body annotation was empty on method %s.",
method.getName());
if (body.indexOf('{') == -1) {
// body中不存在{,直接传入body
data.template().body(body);
} else {
// body中存在{,就是bodyTemplate方式
data.template().bodyTemplate(body);
}
} else if (annotationType == Headers.class) {
// @Header注解
String[] headersOnMethod = Headers.class.cast(methodAnnotation).value();
checkState(headersOnMethod.length > 0, "Headers annotation was empty on method %s.",
method.getName());
data.template().headers(toMap(headersOnMethod));
}
}
//处理参数上的注解
@Override
protected boolean processAnnotationsOnParameter(MethodMetadata data,
Annotation[] annotations,
int paramIndex) {
boolean isHttpAnnotation = false;
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = annotation.annotationType();
if (annotationType == Param.class) {
// @Param注解
Param paramAnnotation = (Param) annotation;
String name = paramAnnotation.value();
checkState(emptyToNull(name) != null, "Param annotation was empty on param %s.",
paramIndex);
// 增加到MethodMetadata中
nameParam(data, name, paramIndex);
Class<? extends Param.Expander> expander = paramAnnotation.expander();
// @Param注解的expander参数,定义参数的解释器,默认是ToStringExpander,调用参数的toString方法
if (expander != Param.ToStringExpander.class) {
data.indexToExpanderClass().put(paramIndex, expander);
}
// 参数是否已经urlEncoded,如果没有,会使用urlEncoded方式编码
data.indexToEncoded().put(paramIndex, paramAnnotation.encoded());
isHttpAnnotation = true;
if (!data.template().hasRequestVariable(name)) {
// 如果参数不在path里面,不在query里面,不在header里面,就设置到formParam中
data.formParams().add(name);
}
} else if (annotationType == QueryMap.class) {
// @QueryMap注解,注解参数对象时,将该参数转换为http请求参数格式发送
checkState(data.queryMapIndex() == null,
"QueryMap annotation was present on multiple parameters.");
data.queryMapIndex(paramIndex);
data.queryMapEncoded(QueryMap.class.cast(annotation).encoded());
isHttpAnnotation = true;
} else if (annotationType == HeaderMap.class) {
// @HeaderMap注解,注解一个Map类型的参数,放入http header中发送
checkState(data.headerMapIndex() == null,
"HeaderMap annotation was present on multiple parameters.");
data.headerMapIndex(paramIndex);
isHttpAnnotation = true;
}
}
return isHttpAnnotation;
}
private static Map<String, Collection<String>> toMap(String[] input) {
Map<String, Collection<String>> result =
new LinkedHashMap<String, Collection<String>>(input.length);
for (String header : input) {
int colon = header.indexOf(':');
String name = header.substring(0, colon);
if (!result.containsKey(name)) {
result.put(name, new ArrayList<String>(1));
}
result.get(name).add(header.substring(colon + 1).trim());
}
return result;
}
}
代码较多,但是逻辑很清晰,先处理类上的注解,再处理方法上注解,最后处理方法参数注解,把所有注解的情况都处理到就可以了。
生成的MethodMetadata的结构如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String configKey;
private transient Type returnType;
private Integer urlIndex;
private Integer bodyIndex;
private Integer headerMapIndex;
private Integer queryMapIndex;
private boolean queryMapEncoded;
private transient Type bodyType;
private RequestTemplate template = new RequestTemplate();
private List<String> formParams = new ArrayList<String>();
private Map<Integer, Collection<String>> indexToName =
new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Collection<String>>();
private Map<Integer, Class<? extends Expander>> indexToExpanderClass =
new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Class<? extends Expander>>();
private Map<Integer, Boolean> indexToEncoded = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Boolean>();
private transient Map<Integer, Expander> indexToExpander;
Contract也是feign的一个扩展点,一个优秀组件的架构通常是具有很强的扩展性,feign的架构本身很简单,设计的扩展点也很简单方便,所以受到spring的青睐,将其集成到spring cloud中。spring cloud就是通过Contract的扩展,实现使用springMVC的注解接入feign。feign自己还实现了使用jaxrs注解接入feign。
初始化总结
上文已经完成了feign初始化结构为动态代理的整个过程,简单的捋一遍:
- 初始化 Feign.Builder 传入参数,构造 ReflectiveFeign
- ReflectiveFeign 通过内部类 ParseHandlersByName 的 Contract 属性,解析接口生成 MethodMetadata
- ParseHandlersByName 根据 MethodMetadata 生成 RequestTemplate 工厂
- ParseHandlersByName 创建 SynchronousMethodHandler,传入 MethodMetadata、RequestTemplate 工厂和 Feign.Builder 相关参数
- ReflectiveFeign 创建 FeignInvocationHandler,传入参数 SynchronousMethodHandler,绑定DefaultMethodHandler
- ReflectiveFeign 根据 FeignInvocationHandler创建 Proxy
关键的几个类是:
- ReflectiveFeign 初始化入口
- FeignInvocationHandler 实现动态代理的 InvocHandler
- SynchronousMethodHandler 方法处理器,方法调用处理器
- MethodMetadata 方法元数据